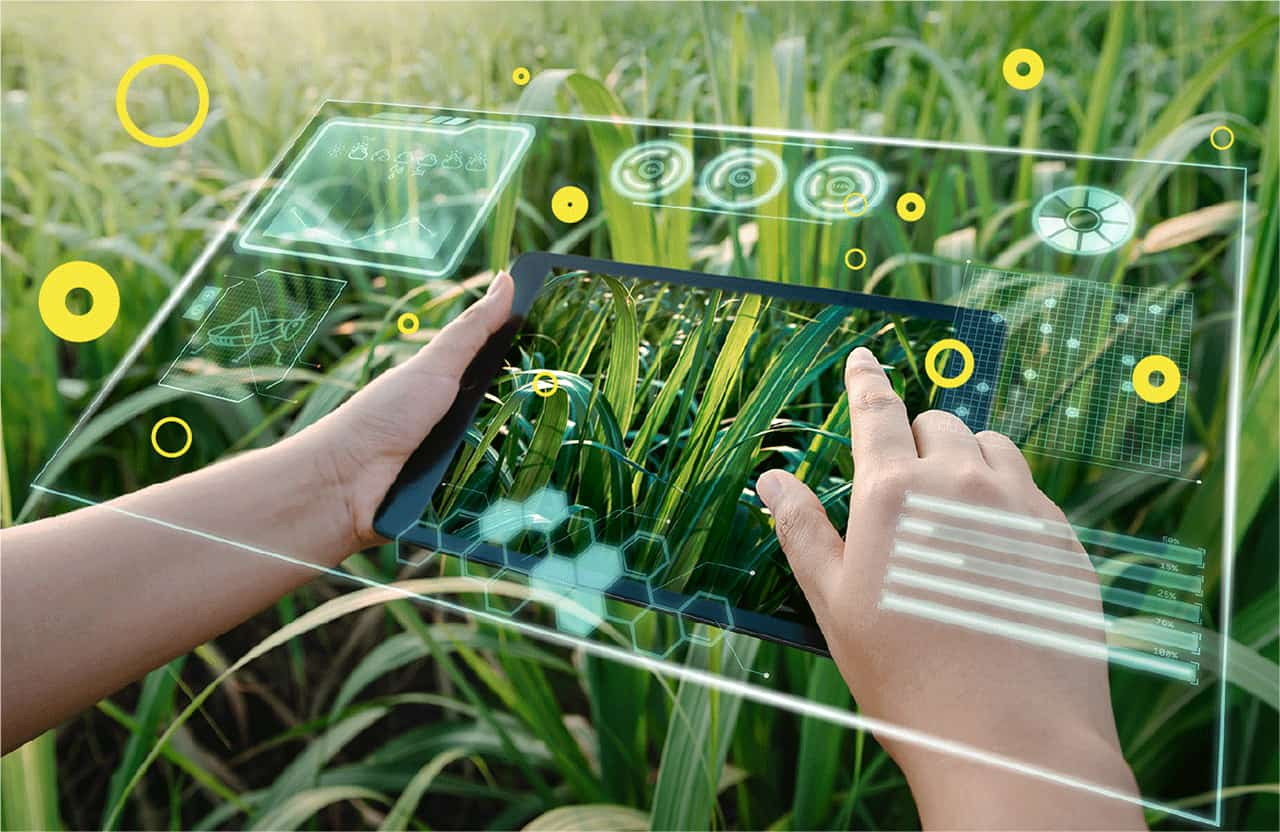
Agriculture is undergoing a powerful transformation as technology reshapes how food is grown, managed, and distributed. With increasing pressure from population growth, climate uncertainty, and limited natural resources, traditional farming practices are no longer sufficient to meet global food demands. This is where data science is making a meaningful impact. By leveraging data-driven insights, modern agriculture is shifting toward smarter, more efficient, and more sustainable farming methods. Data science enables farmers to predict yields, manage risks, and optimize resources, turning agriculture into a precision-driven industry rather than a practice based solely on experience and intuition.
How Data Science is Redefining Agriculture
At its core, data science in agriculture focuses on transforming raw agricultural data into actionable insights. Farms today generate massive amounts of data through sensors, satellite images, drones, weather stations, and smart machinery. This information, when analyzed using machine learning and advanced analytics, helps identify patterns related to crop growth, soil conditions, water usage, and environmental stress. As agriculture becomes more data-centric, professionals trained through a Data Science Course in Chennai are increasingly contributing to the development of intelligent systems that support farmers with accurate predictions and timely recommendations.
Smart Farming Through Real-Time Data
Smart farming represents a shift from reactive decision-making to proactive farm management. Instead of waiting for visible signs of crop stress, data science allows farmers to monitor field conditions in real time. Sensors placed across farmlands collect data on soil moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels. This information is continuously analyzed to guide irrigation schedules, fertilizer application, and crop maintenance. By using data-driven insights, farmers can avoid overuse of resources, reduce costs, and improve overall crop health while minimizing environmental impact.
Precision Agriculture and Efficient Resource Use
One of the most practical applications of data science is precision agriculture. Unlike conventional farming methods that treat an entire field uniformly, precision agriculture focuses on micro-level variations within farmland. Data models analyze differences in soil quality, moisture levels, and crop performance across different sections of a field. This allows farmers to apply water, seeds, and fertilizers only where needed. Such targeted interventions improve yields while conserving resources, making farming both economically and environmentally sustainable.
Yield Prediction for Better Planning
Yield prediction is a game changer for farmers and agribusinesses alike. Accurate yield forecasts help in planning storage, transportation, pricing, and supply chain logistics. Data science enables yield prediction by analyzing historical crop data, weather trends, soil characteristics, and satellite imagery.By identifying intricate correlations between these factors, machine learning algorithms are able to provide projections that are far more accurate than estimates made by hand. Early yield predictions also allow farmers to adjust strategies during the growing season to maximize output and reduce losses.
Weather Intelligence and Climate Adaptation
Weather uncertainty has always been a major risk in agriculture. Data science significantly improves weather-based decision-making by integrating historical climate records with real-time meteorological data. Predictive models can forecast rainfall patterns, temperature changes, drought risks, and extreme weather events. These insights allow farmers to modify planting schedules, select resilient crop varieties, and implement protective measures in advance. Over time, data analysis also helps assess long-term climate trends, supporting sustainable agricultural planning and climate adaptation strategies.
Early Detection of Pests and Crop Diseases
Pests and plant diseases can severely affect crop yields if not identified early. Data science-powered image recognition tools analyze images captured by drones or mobile devices to detect early signs of infestation or disease. By identifying intricate correlations between these factors, machine learning algorithms are able to provide projections that are far more accurate than estimates made by hand. Early detection enables farmers to take timely action, reducing dependence on excessive pesticides and preventing large-scale crop damage.
Data Science Beyond the Farm
The impact of data science extends beyond crop production into the agricultural supply chain. Predictive analytics helps forecast market demand, optimize inventory, and reduce post-harvest losses. Farmers can use market insights to decide the best time to sell their produce, improving profitability. Data-driven supply chain management also enhances food distribution efficiency, ensuring fresher produce reaches consumers while minimizing waste.
Challenges in Agricultural Data Adoption
Despite its advantages, implementing data science in agriculture is not without challenges. Limited digital infrastructure, especially in rural regions, can restrict access to real-time data. Many farmers also lack the technical knowledge required to interpret analytical insights. Furthermore, integrating data from several sources into a single system might be difficult. Overcoming these challenges requires collaboration between governments, technology providers, and educational institutions to promote digital literacy and affordable solutions.
Bridging the Skill Gap Through Education
The effective use of data science in agriculture is strongly dependent on trained experts who can convert complicated insights into actionable advice. Education is really important in this process. Programs such a Data Analytics Course in Chennai teach students how to understand agricultural data, construct prediction models, and convey findings in a way that farmers can readily adopt. These abilities serve to bridge the gap between cutting-edge technology and real-world farming requirements.
The Future of Data-Driven Agriculture
As technologies like artificial intelligence, IoT, and cloud computing continue to advance, data science will become even more central to agriculture. Future farms are expected to rely on autonomous systems, real-time analytics, and highly accurate yield predictions. With continuous innovation, data science has the potential to enhance food security, improve farmer livelihoods, and promote sustainable agricultural practices worldwide.
Data science is transforming agriculture by enabling smarter farming and reliable yield prediction. From precision agriculture and weather forecasting to pest detection and market analysis, data-driven insights are reshaping every stage of the agricultural lifecycle. While challenges remain, ongoing technological advancements and focused education are accelerating adoption. Data science will be essential to creating a robust, effective, and sustainable global food system as agriculture develops.

Leave a Reply